Quickstart#
prose contains the structure to build astronomical images pipelines.
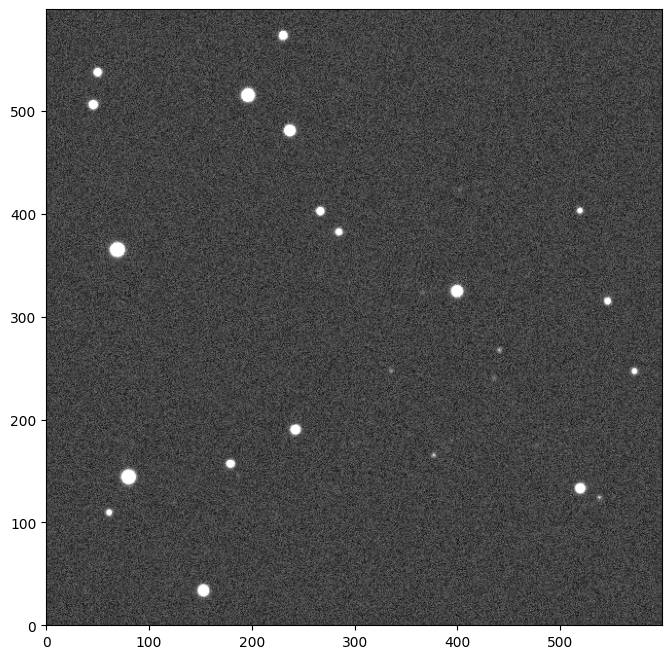
Here is a quick example pipeline to characterize the point spread function (PSF) of an image. Let’s start by loading an example Image.
from prose import Sequence, blocks, example_image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# getting the example image
image = example_image()
image.show()
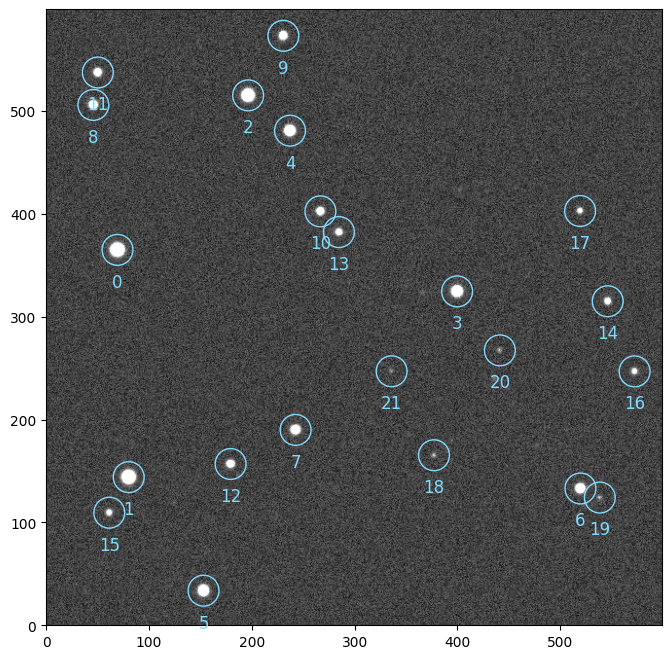
We can now build a Sequence containing single processing units called Block that will sequentially process our image.
sequence = Sequence(
[
blocks.PointSourceDetection(), # stars detection
blocks.Cutouts(21), # cutouts extraction
blocks.MedianEPSF(), # PSF building
blocks.Moffat2D(), # PSF modeling
]
)
sequence.run([image])
# plotting the detected stars
image.show()
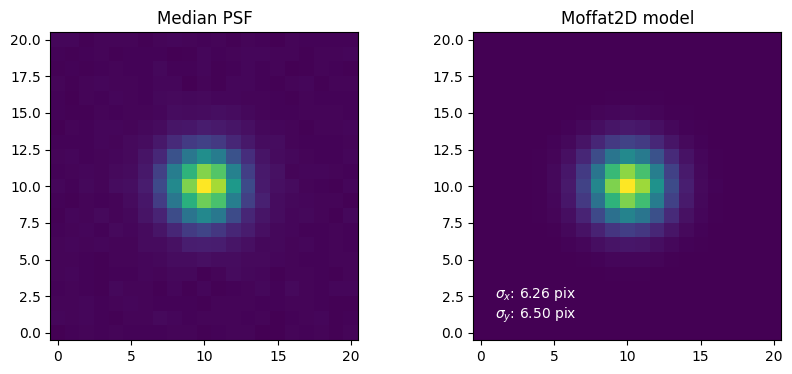
Let’s plot the results of the PSF building and modeling from the Image attributes.
plt.figure(None, (10, 4))
# PSF building
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1, title="Median PSF")
plt.imshow(image.epsf.data, origin="lower")
# PSF modeling
params = image.epsf.params
model = image.epsf.model
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2, title=f"Moffat2D model")
plt.imshow(model(params), origin="lower")
_ = plt.text(
1,
1,
f"$\sigma_x$: {params['sigma_x']:.2f} pix\n$\sigma_y$: {params['sigma_y']:.2f} pix",
c="w",
)
prose contains a wide variety of blocks implementing methods and algorithms commonly used in astronomical image processing.